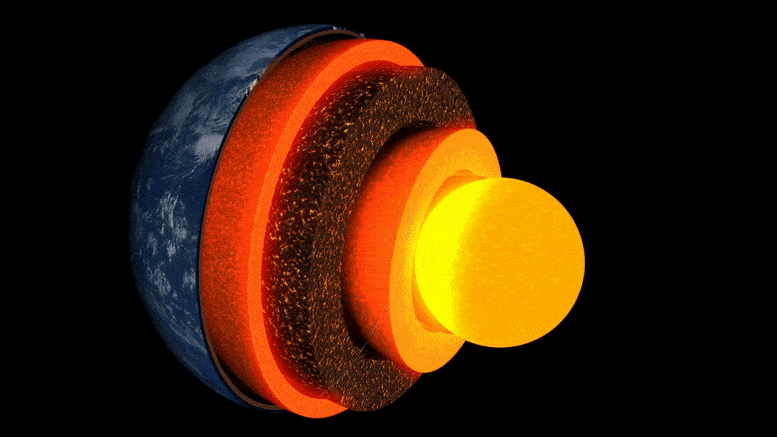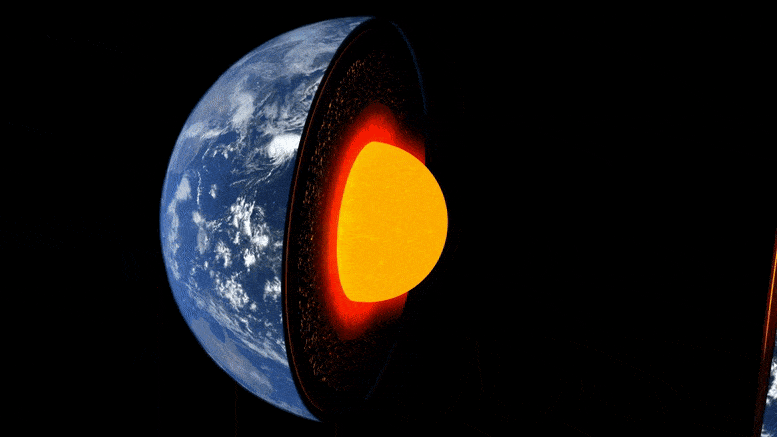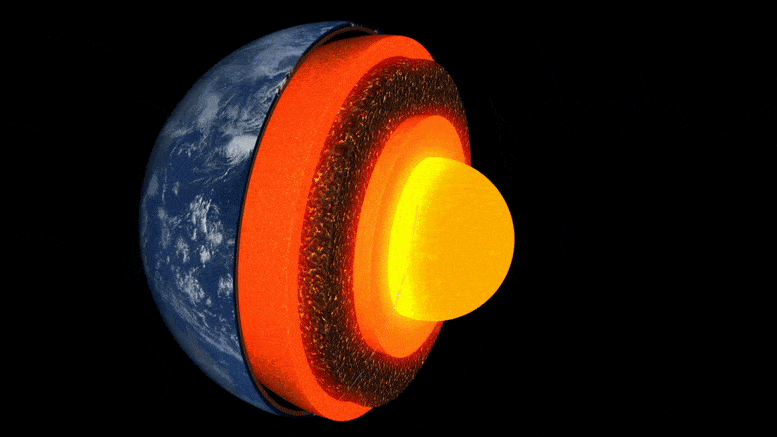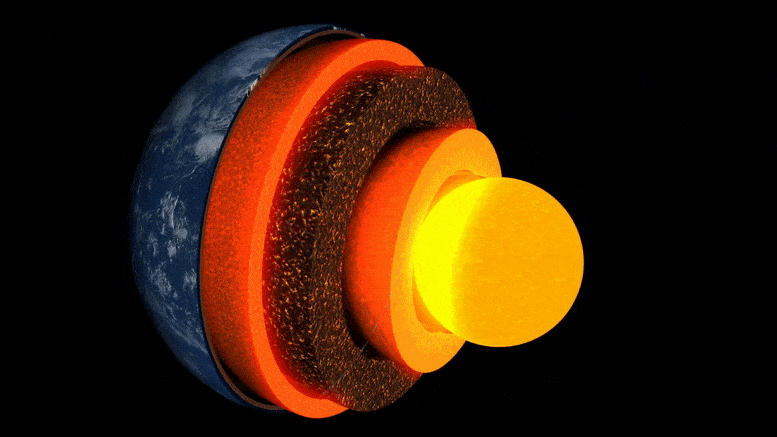
Animasi lapisan bumi.
Penelitian baru yang dipimpin oleh University of Cambridge adalah yang pertama mendapatkan ‘gambar’ rinci dari kantong batu yang tidak biasa di lapisan batas dengan inti bumi, sekitar tiga ribu kilometer di bawah permukaan.
Wilayah bebatuan misterius, yang terletak hampir tepat di bawah Kepulauan Hawaii, adalah salah satu dari beberapa wilayah dengan kecepatan sangat rendah – disebut demikian karena gelombang gempa lambat merayap saat melewatinya.
Penelitian diterbitkan di majalah pada 19 Mei 2022 Komunikasi Alamadalah yang pertama mengungkapkan secara rinci asimetri interior yang kompleks dari salah satu kantong ini, menjelaskan lanskap interior bumi yang dalam dan proses yang beroperasi di dalamnya.
“Dari semua fitur terdalam Bumi, ini adalah yang paling indah dan kompleks.” – seperti saya
“Dari semua fitur internal bumi yang dalam, ini adalah yang paling menarik dan kompleks. Kami sekarang telah memperoleh bukti kuat pertama yang menunjukkan struktur internalnya – ini adalah tengara sejati dalam seismologi dalam,” kata penulis utama Zhi Li, seorang mahasiswa PhD di Departemen Ilmu Bumi di Cambridge.ground”.
Bagian dalam Bumi terbentuk seperti bawang: di tengahnya adalah inti besi-nikel, dikelilingi oleh lapisan tebal yang dikenal sebagai mantel, dan di atasnya ada kerak luar yang tipis – kerak tempat kita hidup. Meskipun mantel adalah batuan padat, cukup panas sehingga mengalir sangat lambat. Arus konveksi internal memberi panas ke permukaan, menyebabkan pergerakan lempeng tektonik dan memicu letusan gunung berapi.
Para ilmuwan menggunakan gelombang seismik dari gempa bumi untuk “melihat” apa yang ada di bawah permukaan bumi—gema dan bayangan gelombang ini mengungkapkan gambar seperti radar dari interior dalam. Namun hingga saat ini, “gambar” struktur pada batas inti-mantel, wilayah yang menjadi perhatian utama untuk mempelajari aliran panas internal planet kita, masih buram dan sulit untuk ditafsirkan.

Peristiwa dan lintasan sinar Sdiff yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini. a) Penampang melintang yang memotong pusat wilayah kecepatan ultra-rendah di Hawaii, menunjukkan lintasan sinar untuk gelombang Sdiff pada 96°, 100, 110°, dan 120° untuk model Bumi 1D PREM. Garis putus-putus dari atas ke bawah menunjukkan diskontinuitas 410 km, 660 km, dan 2.791 km (100 km di atas batas inti-mantel). b) Peristiwa dan lintasan sinar Sdiff pada model tomografi latar SEMUCB_WM1 pada kedalaman 2791 km. Bola pantai untuk acara yang dicat dalam berbagai warna termasuk 20100,320 (kuning), 20111214 (hijau), 20120417 (merah), 20180910 (ungu), 20180518 (coklat), 20181030 (merah muda), 20161122 (abu-abu), stasiun (segitiga) , dan sinar. Lintasan gelombang sdiff pada kedalaman lubang 2.791 km pada mantel bawah yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini. Peristiwa yang digunakan dalam analisis periode pendek disorot dengan warna kuning. Lokasi ULVZ yang diusulkan ditampilkan dalam lingkaran hitam. Garis putus-putus menunjukkan penampang yang digambar di A. Kredit: Nature Communications, DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-30502-5
Para peneliti menggunakan metode pemodelan numerik mutakhir untuk mendeteksi struktur skala kilometer di batas inti-mantel. Menurut rekan penulis Dr. Kuangdai Leng, yang mengembangkan metode saat berada di[{” attribute=””>University of Oxford, “We are really pushing the limits of modern high-performance computing for elastodynamic simulations, taking advantage of wave symmetries unnoticed or unused before.” Leng, who is currently based at the Science and Technology Facilities Council, says that this means they can improve the resolution of the images by an order of magnitude compared to previous work.
The researchers observed a 40% reduction in the speed of seismic waves traveling at the base of the ultra-low velocity zone beneath Hawaii. This supports existing proposals that the zone contains much more iron than the surrounding rocks – meaning it is denser and more sluggish. “It’s possible that this iron-rich material is a remnant of ancient rocks from Earth’s early history or even that iron might be leaking from the core by an unknown means,” said project lead Dr Sanne Cottaar from Cambridge Earth Sciences.

Conceptual cartoons of the Hawaiian ultra-low velocity zone (ULVZ) structure. A) ULVZ on the core–mantle boundary at the base of the Hawaiian plume (height is not to scale). B) a zoom in of the modeled ULVZ structure, showing interpreted trapped postcursor waves (note that the waves analyzed have horizontal displacement). Credit: Nature Communications, DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-30502-5
The research could also help scientists understand what sits beneath and gives rise to volcanic chains like the Hawaiian Islands. Scientists have started to notice a correlation between the location of the descriptively-named hotspot volcanoes, which include Hawaii and Iceland, and the ultra-low velocity zones at the base of the mantle. The origin of hotspot volcanoes has been debated, but the most popular theory suggests that plume-like structures bring hot mantle material all the way from the core-mantle boundary to the surface.
With images of the ultra-low velocity zone beneath Hawaii now in hand, the team can also gather rare physical evidence from what is likely the root of the plume feeding Hawaii. Their observation of dense, iron-rich rock beneath Hawaii would support surface observations. “Basalts erupting from Hawaii have anomalous isotope signatures which could either point to either an early-Earth origin or core leaking, it means some of this dense material piled up at the base must be dragged to the surface,” said Cottaar.
More of the core-mantle boundary now needs to be imaged to understand if all surface hotspots have a pocket of dense material at the base. Where and how the core-mantle boundary can be targeted does depend on where earthquakes occur, and where seismometers are installed to record the waves.
The team’s observations add to a growing body of evidence that Earth’s deep interior is just as variable as its surface. “These low-velocity zones are one of the most intricate features we see at extreme depths – if we expand our search, we are likely to see ever-increasing levels of complexity, both structural and chemical, at the core-mantle boundary,” said Li.
They now plan to apply their techniques to enhance the resolution of imaging of other pockets at the core-mantle boundary, as well as mapping new zones. Eventually, they hope to map the geological landscape across the core-mantle boundary and understand its relationship with the dynamics and evolutionary history of our planet.
Reference: “Kilometer-scale structure on the core–mantle boundary near Hawaii” by Zhi Li, Kuangdai Leng, Jennifer Jenkins and Sanne Cottaar, 19 May 2022, Nature Communications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-30502-5

“Gamer yang sangat menawan. Ahli web. Sarjana TV. Pecandu makanan. Ninja media sosial yang rajin. Pelopor musik hardcore.”




More Stories
Sebuah studi baru menantang teori oksidasi mantel
Generasi Milenial dan Generasi X menghadapi risiko lebih tinggi terkena 17 jenis kanker ini dibandingkan generasi baby boomer: ScienceAlert
Sebuah pencapaian penting bagi NASA dalam menemukan exoplanet